算法训练营第八周 位运算/布隆过滤器/LRU缓存/排序算法
2021/3/18大约 4 分钟
第八周学习笔记
一、位运算
运算符及含义
| 运算符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| << | 左移 |
| >> | 右移 |
| >>> | 无符号右移 |
| & | 按位与 |
| | | 按位或 |
| ~ | 按位取反 |
| ^ | 按位异或 |
位运算要点
•判断奇偶 x % 2 == 1 ——> (x & 1) == 1
x % 2 == 0 ——> (x & 1) == 0
•除以2 x >> 1 ——> x / 2.
即: x = x / 2; ——> x = x >> 1
mid = (left + right) / 2; ——> mid = (left + right) >> 1
•X = X & (X - 1) 清零最低位的 1
•X & (-X) 得到最低位的 1
•X & ~X => 0
二、LRU Cache
最近最少使用的被替换 查询 O(1), 修改O(1)
Java实现
class LRUCache {
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode pre;
DLinkedNode next;
}
/**
* Always add the new node right after head;
*/
private void addNode(DLinkedNode node) {
node.pre = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.pre = node;
head.next = node;
}
/**
* Remove an existing node from the linked list.
*/
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
DLinkedNode pre = node.pre;
DLinkedNode post = node.next;
pre.next = post;
post.pre = pre;
}
/**
* Move certain node in between to the head.
*/
private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
this.removeNode(node);
this.addNode(node);
}
// pop the current tail.
private DLinkedNode popTail() {
DLinkedNode res = tail.pre;
this.removeNode(res);
return res;
}
private HashMap cache;
private int len;
private int cap;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
cache = new HashMap();
this.len = 0;
this.cap = capacity;
head = new DLinkedNode();
head.pre = null;
tail = new DLinkedNode();
tail.next = null;
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1; // should raise exception here.
}
// move the accessed node to the head;
this.moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode();
newNode.key = key;
newNode.value = value;
this.cache.put(key, newNode);
this.addNode(newNode);
++len;
if (len > cap) {
// pop the tail
DLinkedNode tail = this.popTail();
this.cache.remove(tail.key);
--len;
}
} else {
// update the value.
node.value = value;
this.moveToHead(node);
}
}
}
三、布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器可以用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中。
布隆过滤器说不存在的元素一定不存在。
布隆过滤器说存在的元素不一定存在。
四、排序算法
排序算法可分为基于比较的排序算法和非基于比较的排序算法。
基于比较的排序算法有:选择排序,冒泡排序,插入排序,希尔排序,堆排序,快速排序,归并排序。
非比较类排序有:计数排序,计数排序,桶排序。
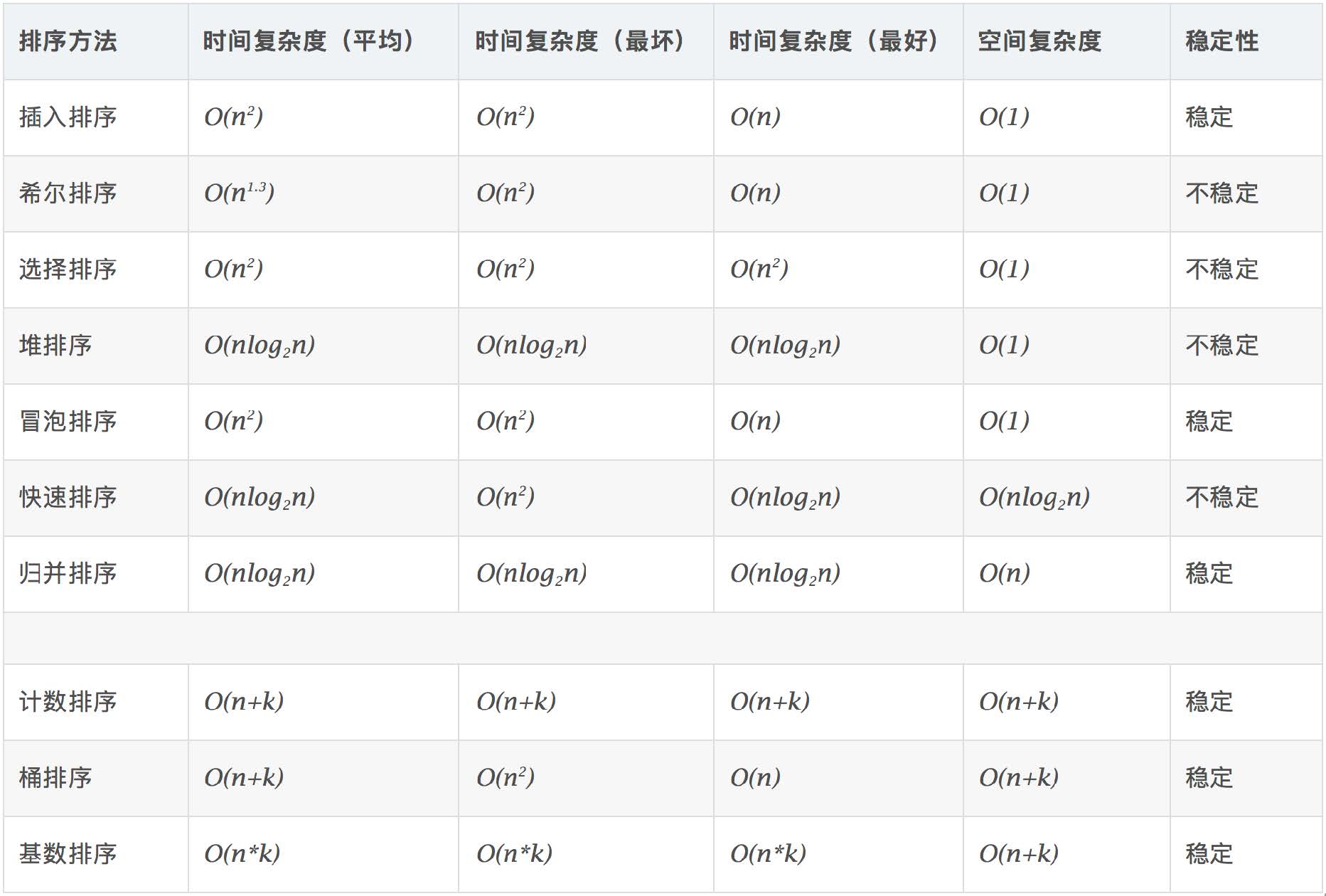
各算法的时间和空间复杂度
1.冒泡排序
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < arr.length - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
2.选择排序
public static void selectionSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[i]) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
### 3.插入排序
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = temp;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
### 4.希尔排序
public static void hillSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
for (int gap = arr.length / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) {
for (int i = gap; i < arr.length; i++) {
int j = i;
while (j - gap >= 0 && arr[j] < arr[j - gap]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
arr[j - gap] = temp;
j -= gap;
}
}
}
}
### 5.堆排序
public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int i : arr) {
pq.offer(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = pq.poll();
}
}
### 6.快速排序
public static void quickSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
if (begin >= end) {
return;
}
int pivot = partition(arr, begin, end);
quickSort(arr, 0, pivot - 1);
quickSort(arr, pivot + 1, end);
}
public static int partition(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
int pivot = end, counter = begin;
for (int i = begin; i < end; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[pivot]) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[counter];
arr[counter] = temp;
counter++;
}
}
int temp = arr[pivot];
arr[pivot] = arr[counter];
arr[counter] = temp;
return counter;
}
### 7.二路归并排序
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
if (begin >= end) {
return;
}
int mid = begin + ((end - begin) >> 1);
mergeSort(arr, begin, mid);
mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, end);
merge(arr, begin, end, mid);
}
private static void merge(int[] arr, int begin, int end, int mid) {
int[] temp = new int[end - begin + 1];
int i = begin, j = mid + 1, k = 0;
while (i <= mid && j <= end) {
temp[k++] = arr[i] < arr[j] ? arr[i++] : arr[j++];
}
while (i <= mid) {
temp[k++] = arr[i++];
}
while (j <= end) {
temp[k++] = arr[j++];
}
for (int p = 0; p < temp.length; p++) {
arr[begin + p] = temp[p];
}
}
### 8.计数排序
当max很大时,计数排序无法使用
public static void countingSort(int[] arr, int max) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int[] count = new int[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
count[arr[i]]++;
}
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= max; i++) {
while (count[i]-- > 0) {
arr[k++] = i;
}
}
}
